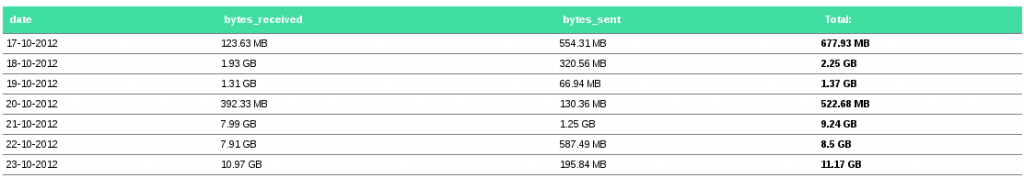
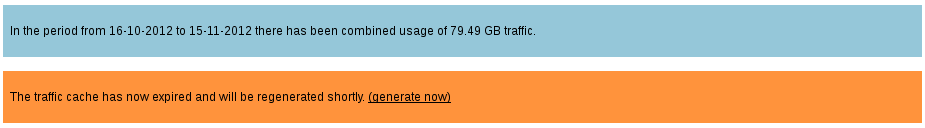
A few weeks ago I wrote about the awesomeness that is Mozilla’s Firefox Sync, a built-in feature of Firefox versions 4 & later which allows for synchronization of bookmarks, history, tabs and password information between multiple systems. (historically known as Weave)
I’ve been running this for a few weeks now on my servers using fully packaged components and it’s been working well, excluding a few minor hick-ups.
It’s taken a bit longer than I would have liked, but I now have stable RPM packages for RHEL/CentOS 5 and 6 for both i386 and x86_64 available publicly.
I always package all software I use on my servers (and even my desktops most of the time) as it makes re-building, upgrading and supporting systems far easier in the long run. By having everything in packages and repos, I can rebuild a server entirely simply by knowing what list of packages were originally installed and their configuration files.
Packaging one’s software is also great when upgrading distribution, as you can get a list of all non-vendor programs and libraries installed and then use the .src.rpm files to build new packages for the new OS release.
Packaging Headaches
Mozilla Sync Server was much more difficult to package than I would have liked, mostly due to the documentation clarity and the number of dependencies.
The primary source of pain was that I run CentOS 5 for a lot of my production systems,which ships with Python 2.4, whereas to run Mozilla Sync Server, you will need Python 2.6 or later.
This meant that I had to build RPMs for a large number (upwards of 20 IIRC) python packages to provide python26 versions of existing system packages. Whilst EPEL had a few of the core ones (such as python26 itself), many of the modules I needed either weren’t packaged, or were only had EPEL packages for Python 2.4.
The other major headache was due to unclear information and in some cases, incorrect documentation from Mozilla.
Mozilla uses the project source name of server-full in the setup documentation, however this isn’t actually the entire “full” application – rather it provides the WSGI executable and some libraries, however you also need server-core, server-reg and server-storage plus a number of python modules to build a complete solution.
Sadly this isn’t entirely clear to anyone reading the setup instructions, the only setup information relates to checking out server-full and running a build script which will go through and download all the dependencies (in theory, it often broke for me) and build a working system, complete with paster web server.
Whilst this would be a handy resource for anyone doing development, it’s pretty useless for someone wanting to package a proper system for deployment since you need to break all the dependencies into separate packages.
(Note that whilst Mozilla refer to having RPM packages for the software components, these have been written for their own inhouse deployment and are not totally suitable for stock systems, not to mention even when you have SPEC files for some of the Mozilla components, you still lack the SPEC files for dependencies.)
To top it off, some information is just flat out wrong and can only be found out by first subscribing to the developer mailing list – in order to gain a login to browse the list archives – so that you can ind such gems as “LDAP doesn’t work and don’t try as it’s being re-written”.
Toss in finding a few bugs that got fixed right around the time I was working on packaging these apps and you can understand if I’m not filled with love for the developers right this moment.
Of course, this is a particularly common open source problem – the team clearly released in a way that made sense to them, and of course everyone would know the difference between server-core/full/reg/storage, etc right?? ;-) I know I’m sometimes guilty of the same thing.
Having said that, the documentation does appear to be getting better and the community is starting to contribute more good documentation resources. I also found a number of people on the mailing list quite helpful and the Mozilla Sync team were really fast and responsive when I opened a bug report, even when it’s a “stupid jethro didn’t hg pull the latest release before testing” issue.
Getting My Packages
All the new packages can be found in the Amberdms public package repositories, the instructions on setting up the CentOS 5 or CentOS 6 repos can be found here.
RHEL/CentOS 5 Repo Instructions
If you are running RHEL/CentOS 5, you only need to enable amberdms-os, since all the packages will install in parallel to the distribution packages. Nothing in this repo should ever clash with packages released by RedHat, but may clash/be newer than dag or EPEL packages.
RHEL/CentOS 6 Repo Instructions
If you are running RHEL/CentOS6, you will need to enable both amberdms-os and amberdms-updates, as some of the python packages that are required are shipped by RHEL, but are too outdated to be used for Mozilla Sync Server.
Note that amberdms-updates may contain newer versions of other packages, so take care when enabling it, as I will have other unrelated RPMs in there. If you only want my newer python packages for mozilla sync, set includepkgs=python-* for amberdms-updates
Also whilst I have tested these packages for Mozilla Sync Server’s requirements, I can’t be sure of their suitability with existing Python applications on your server, so take care when installing these as there’s always a chance they could break something.
RHEL/CentOS 5 & 6 Installation Instructions
Prerequisites:
- Configured Amberdms Repositories as per above instructions.
- Working & configured Apache/httpd server. The packaged programs will work with other web servers, but you’ll have to write your own configuration files for them.
Installation Steps:
- Install packages with:
yum install mozilla-sync-server
- Adjust Apache configuration to allow access from desired networks (standard apache IP rules).
/etc/httpd/conf.d/mozilla-sync-server.conf
- Adjust Mozilla Sync Server configuration. If you want to run with the standard sqllite DB (good for initial testing), all you must adjust is line 44 to set the fallback_node value to the correct reachable URL for Firefox clients.
vi /etc/mozilla-sync-server/mozilla-sync-server.conf
- Restart Apache – due to the way mozilla-sync-server uses WSGI, if you make a change to the configuration, there might still be a running process using the existing config. Doing a restart of Apache will always fix this.
/etc/init.d/httpd restart
- Test that you can reach the sync server location and see if anything breaks. These tests will fail if something is wrong such as missing modules or inability to access the database.
http://host.example.com/mozilla-sync/
^ should return 404 if working - anything else indicated error
http://host.example.com/mozilla-sync/user/1.0/a/
^ should return 200 with the page output of only 0
- There is also a heartbeat page that can be useful when doing automated checks of the service health, although I found it possible to sometimes break the server in ways that would stop sync for Firefox, but still show OK for heartbeat.
http://host.example.com/mozilla-sync/__heartbeat__
- If you experience any issues with the test URLs, check /var/log/httpd/*error_log*. You may experience problems if you’re using https:// with self-signed certificates that aren’t installed in the browser as trusted too, so import your certs properly so they’re trusted.
- Mozilla Sync Server is now ready for you to start using with Firefox clients. My recommendation is to use a clean profile you can delete and re-create for testing purposes and only add sync with your actual profile once you’ve confirmed the server is working.
Using MySQL instead of SQLite:
I tend to standardise on using MySQL where possible for all my web service applications since I have better and more robust monitoring and backup tools for MySQL databases.
If you want to setup Mozilla Sync Server to use MySQL, it’s best to get it working with SQLite first and then try with MySQL to ensure you don’t have any issues with the basic setup before doing more complex bits.
- Obviously the first step should be to setup MySQL server, if you haven’t done this yet, the following command will set it up and take you through a secure setup process to password protect the root DB accounts:
yum install -y mysql-server
/etc/init.d/mysqld start
chkconfig --level 345 mysqld on
/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
- Once the MySQL server is running, you’ll need to create a database and user for Mozilla Sync Server to use – this can be done with:
mysql -u root -p
# or without -p if no MySQLroot password
CREATE DATABASE mozilla_sync;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON mozilla_sync.* TO mozilla_sync@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'examplepassword';
flush privileges;
\q
- Copy the [storage] and [auth] sections from /etc/mozilla-sync-server/sample-configs/mysql.conf to replace the same sections in /etc/mozilla-sync-server/mozilla-sync-server.conf. The syntax for the sqluri line is:
sqluri = mysql://mozilla_sync:examplepassword@localhost:3306/mozilla_sync
- Restart Apache (very important, failing todo so will not apply config changes):
/etc/init.d/httpd restart
- Complete! Test from a Firefox client and check table structure is created with SHOW TABLES; MySQL query to confirm successful configuration.
Other Databases
I haven’t done any packaging or testing for it, but Mozilla Sync Server also supports memcached as a storage database, there is a sample configuration file supplied with the RPMs I’ve built, but you may need to also built some python26 modules to support it.
Other Platforms?
If you want to package for another platform, the best/most accurate resource on configuring the sync server currently is one by Fabian Wenk about running it on FreeBSD.
I haven’t seen any guides to packaging the application, the TL;DR version is that you’ll essentially need server-full, server-core, server-reg and server-storage, plus all the other python-module dependencies – take a look at the RPM specfiles to get a good idea.
I’ll hopefully do some Debian packages in the near future too, will have to work on improving my deb packaging foo.
Warnings, issues, small print, etc.
These packages are still quite beta, they’ve only been tested by me so far and there’s possibly some things in them that are wrong.
I want to go through and clean up some of the Python module RPMs at some stage as I don’t think the SPEC files I have are as portable as they should be, commits back always welcome. ;-)
If you find these packages useful, please let me know in comments or emails, always good to get an idea how people find this stuff and whether it’s worth the late nighters. ;-)
And if you have any problems, feel free to email me or comment on this page and I’ll help out the best I can – I suspect I’ll have to write a Mozilla Sync Server troubleshooting guide at some stage sooner or later.